What is Telemedicine: Ultimate Guide
In this post covid era, we rely on technology for everything. Everything is done with a few clicks from the comfort of your home, from ordering food to making bookings! As the covid-19 spread, the healthcare industry experienced a significant surge. One such revolution that completely revamped this industry is the introduction of telemedicine software, where patients get the best healthcare services remotely. As a medical professional, if you want to know about telemedicine and how it works, you have landed on the right page. This article is a complete guide on what is telemedicine. So, here we go!
Table of Contents
- History of Telemedicine
- What is Telemedicine Services?
- What is Telehealth?
- Applications of Telemedicine
- Difference Between Telemedicine and Telehealth
- How Telemedicine Services Works
- How to Improve Telemedicine in Healthcare?
- Why is Telemedicine Services Important in Healthcare?
- Telemedicine Services Pros and Cons
- Types of Telemedicine Services
- Top Telemedicine Services Medical Specialties
- What services can be provided by Telemedicine Services
- Telemedicine Services Regulations
- Barriers to Telemedicine Services
- HIPAA and Telemedicine Services
- Telemedicine Services Terms
- Step-by-step process of telemedicine app development
- The Future of Telehealth
- Understanding Telemedicine Terms
- Conclusion
- FAQs
History of Telemedicine
Many people consider Telemedicine app a new and state-of-the-art innovation since it includes the interaction of doctors and patients through video screens. You’ll be surprised to know that Telemedicine goes as far back as 500 BCE in old Rome and Greece, where human messengers sent medical advice. As far as we might be concerned, present-day Telemedicine is firmly connected with the improvement of information technology and communication.
In April 1924, a Radio News magazine issue showed a patient speaking with a specialist through TV and a microphone. This idea would soon be the future, despite American homes barely embracing the radio and many individuals didn’t have TVs. By the last part of the 1950s and mid-1960s, video transmission in Telemedicine began with the University of Nebraska leading the charge. The growth in internet usage during the 1990s encouraged more development in Telemedicine, as we are witnessing today.
What is Telemedicine Services?
Telemedicine definition utilizes instruments that permit patients to get medical care and further improve engagement with telecommunication technologies. This innovation makes it easier for individuals in advantages of telemedicine in rural areas and remote areas to get treatment without traveling long distances. Doctors can easily communicate with their patients in real-time and transfer essential information for their well-being.
Telemedicine’s popularity has just been slowed by some doctors’ reluctance to adopt the practice in their healthcare systems. In any case, the constant advancement of technology guarantees the improvement of this field in the coming years. Recently, there has been a massive adoption due to a new generation of technology-focused patients and the COVID-19 pandemic that encouraged people to stay at home.
What is Telehealth?
Telehealth is the use of different digital technologies and tools like mobile devices and computers to access excellent healthcare services remotely. Using this technology, patients do not have to physically visit the doctor’s clinic. Whereas, doctors provide quality medical services online. Telehealth encompasses different services, such as:
- Remote patient monitoring
- Virtual consultations
- Electronic transmission of medical records.
The major aim of this app is to make healthcare services accessible. In telehealth, major technologies are mobile health apps, video conferencing, online health portals, and wearable devices. Through efficient and timely healthcare delivery, telehealth supports excellent chronic conditions management and promotes patient satisfaction.
Applications of Telemedicine
After knowing what is telemedicine, now here are some major telemedicine applications:
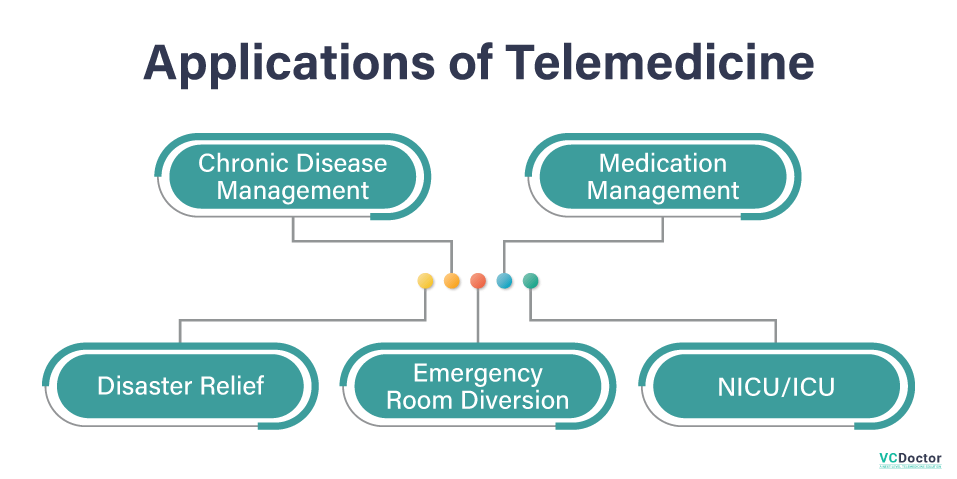
1. Chronic disease management
Thanks to advanced medical technology, Doctors can now remotely check their patients’ health. Through data transfer from one device to another, touchscreen technology gives healthcare professionals access to heart rate, blood pressure, glucose levels, and more.
Telemedicine promotes medical facilities treating patients with long-term conditions. Therefore, they have developed telemedicine technologies that enable doctors to stay informed while working from home or at a hospital. In the process of providing patient care, the patient, their family, and other medical experts can work together.
2. Medication management
Healthcare professionals understand how vital drug control is, particularly for senior citizens. Telemedicine is helpful since older adults tend to forget about their medicines. This telehealth technology allows doctors and other professionals to track their patients’ medicines. Furthermore, this reduces readmissions to hospitals and improves medication compliance.
3. Disaster relief
In case of any disaster, local healthcare resources are pulled rapidly to offer emergency and non-emergency care. This causes a shortage of supply as the demand is higher. With the help of telemedicine technology, remote healthcare services can be provided through remote consultations. This ensures healthcare providers can focus on highly complex cases.
4. Emergency room diversion
The emergency room is the most crowded and stressful environment in the healthcare industry. Since patients can now be seen online with the help of technology, overcrowded medical emergency rooms are reduced. Further, your remote doctor decides if the patient requires emergency care or not!
5. NICU/ICU
Telemedicine can be applied in many different ways in the NICU/ICU. Using HD webcams to view the infant from various perspectives is one method. A specialist at another hospital can see high-risk infants in a matter of seconds by just transmitting the footage.
This lessens the necessity for babies to undergo the time-and money-consuming transfer to another facility. Additionally, some facilities have scheduled telemedicine follow-up visits for a week following a baby’s release from the NICU. Hospitals that took this action reported a notable drop in additional visits or calls from anxious parents.
Difference Between Telemedicine and Telehealth
| Aspect | Telemedicine | Telehealth |
| Definition | Use of telecommunications technology for clinical services | Use of telecommunications technology for a broader range of health services |
| Focus | Clinical services | All health services, including non-clinical services |
| Example | Remote consultations between doctors and patients, remote diagnosis and treatment | Remote patient education, administrative meetings, training for healthcare staff |
| Scope | Narrow, focusing on direct patient care | Broad, encompassing all aspects of healthcare delivery |
| Usage | Diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up care | Health education, health system management, non-clinical services |
Telemedicine and Telehealth are related terms. Even sometimes, some publications and organizations use these terms interchangeably by some publications and organizations. However, there is a difference in both of these terms. According to HealthID.org, Telehealth utilizes electronic data and telecommunications technologies to help and promote long-distance clinical healthcare, patient and expert health education, public health, and health administration.
Telehealth is a more extensive category that incorporates all aspects of healthcare, including nonclinical exercises like physical training, administrative meetings, and continuing medical education (CME). Telemedicine services only allude to remote clinical services like diagnosis and treatment. At the same time, Telehealth software incorporates all the technologies that help in improving healthcare services and their delivery. So Telemedicine is a category under telehealth services as it has a considerable scope.
How Telemedicine Services Works
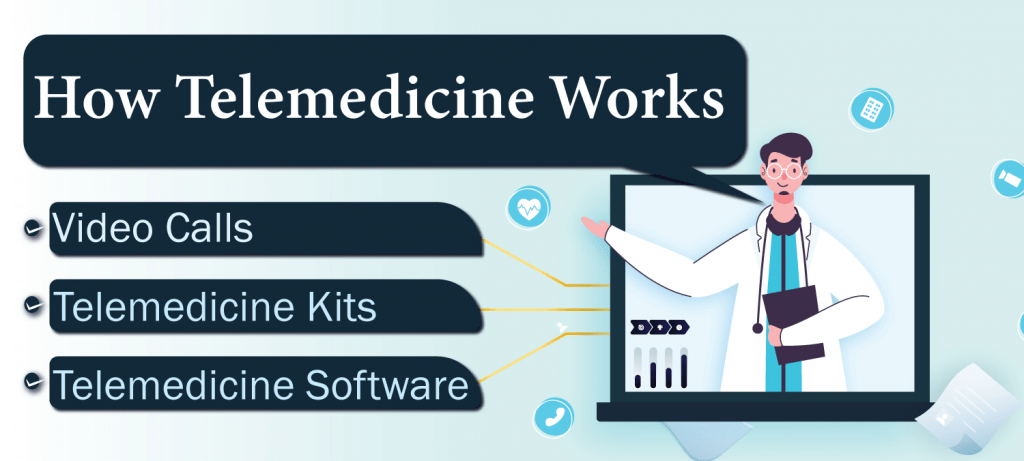
Healthcare institutions use Telemedicine services in several ways based on the health institutions and requirements of the patient. Here is how does telemedicine work!
Video Calls
This is the essential and most widely used telemedical medium between doctors and patients. It resembles an ordinary video call between companions. In many nations, HIPAA guidelines guarantee all video calls are through secure video conferencing software.
Telemedicine Kits
Portable tele medicine packs that utilize mobile medical devices and PCs like vital-signs monitors and ECGs for telemedicine practice. Doctors utilize advanced cameras to send detailed images to experts who analyze them and give proper diagnoses and treatment strategies.
Telemedicine Software
Institutions can utilize specific telemedicine platforms that offer services, including live video conferencing in healthcare and data storage. This software meets up with improvements and patient necessities.
How to Improve Telemedicine in Healthcare?
For telemedicine billing services to be compelling, medical institutions need to gather legitimate data for better service delivery. The framework configuration ought to pose appropriate inquiries speedily, like pregnancy status, weight, previous circumstances, etc., to recommend the right medicines. Telemedicine software ought to be faultless if the design protocols inputted by people are substantial.
One method for working on the productivity of Telemedicine services and conveying results that are equivalent to one-on-one encounters is to lessen documentation time by placing unstructured information into electronic health records. Likewise, patients could connect quickly by utilizing a technique that associates them to the nearest accessible doctor in their time of need – similar to the Uber systems. This way, an accessible specialist makes a call to the patient, and the patient gets a consultation.
Why is Telemedicine Services Important in Healthcare?
Technology now plays a vital role in healthcare. Its integration in access into our daily life makes it more significant than ever. With a cell phone, it’s now easier to track and monitor medical cycles while getting therapy and treatment from the comfort of your home. In instances of infectious diseases, it additionally decreases the chance of transmission and expands security.
The American Telemedicine Association expresses that Telemedicine in healthcare can deal with more than 70% of urgent medical illnesses, prompting a speedy and efficient diagnosis. Many individuals need steady medical care yet don’t have access to quality services for geological or monetary reasons. In several regions of the world where quality healthcare requires travel, telemedicine assists with overcoming that issue and gives access to those who are in need.
Telemedicine Services Pros and Cons
Telemedicine in healthcare is a persistently developing idea and offers a ton of advantages. Still, some challenges are needed to be overcome. Have a look at some of the telemedicine pros and cons.
Pros of Telemedicine
- Patients get simpler access to experts in their time of need. Even doctors can easily be referred without worrying about their proximity.
- It makes patient care more accessible and convenient to a lot of individuals.
- Care telemedicine appointments are effortlessly monitored and kept up with by drawing patients through telemedicine channels.
- Telemedicine helps save the expense of transportation and service charges for the patients. Health institutions not only save money with remote monitoring services but also store data efficiently.
- Telemedicine gives doctors additional opportunities to focus on patients and give more attention, accordingly working on the improved quality of service.
Cons of Telemedicine
- It costs cash and a great deal of time to set up a legitimate and powerful telemedicine stage. Hardware expenses, preparing, and rebuilding staff liabilities are only a few perspectives to consider prior to building a telemedicine stage.
- Telemedicine is a ceaselessly evolving industry. Subsequently, it is vulnerable to new regulations, strategies, and guidelines that could adversely influence the patients or medical services suppliers.
Types of Telemedicine Services
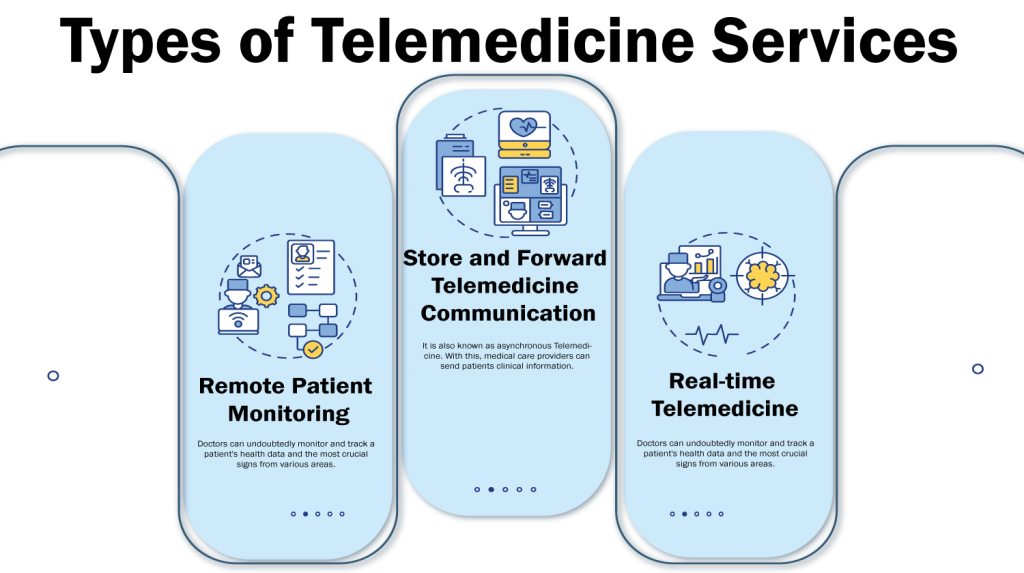
At the point when most people attempt to picture Telemedicine in real life, they see it as a specialist taking care of a patient through video call, yet it’s a lot more extensive than that. The primary kinds of Telemedicine are:
Remote Patient Monitoring
Doctors can undoubtedly monitor and track a patient’s health data and the most crucial signs from various areas. Assuming there are any warning signs, the doctor will recognize them and intervene appropriately with the help of hipaa compliant telemedicine software for patients.
Real-time Telemedicine Services
Real-time Telemedicine is the most commonly known type of Telemedicine service. It includes communication through audio and video between a patient and a medical care professional. Moreover, It should substitute for an in-person visit so the doctor can convey real-time diagnosis and support with HIPAA Compliant Telehealth Platform.
Store and Forward Telemedicine Services Communication
It is also known as asynchronous Telemedicine. With this, medical care providers can send patients clinical information. For example, images, lab results, recordings, and records to medical care faculty in another location. Data submitted on these platforms are secure, so confidential patient data can remain confidential.
Top Telemedicine Services Medical Specialties
Some medical specialties easily adapted to telemedicine services, and over the years, they have become more famous for use in Telemedicine than others. They are:
Telenephrology: Nephrology practice is valuable in inter-professional instances when a doctor needs to counsel a nephrologist about a patient’s kidney condition.
Telepsychiatry: Psychiatry doesn’t normally need the same examination as other clinical fields. Alongside a lack of available psychiatrists, this has made ROI With Telepsychiatry very famous.
Telerehabilitation: Rehabilitation services conveyed remotely through Telemedicine solutions can provide many advantages to both the doctors and patients.
Teleradiology: This is probably the earliest field of Telemedicine. It permits providers to send the x-ray of a patient to a radiologist and get speedy consultation for the patient.
Small hospitals with the unavailability of in-house radiologists round the clock take advantage of Teleradiology predominantly.
Teledermatology: Teledermatology services work by sending an image of a mole, rash, or other skin irregularities to a dermatologist for quick diagnosis and treatment options.
Teleoncology: Oncologists contact their patients through video platforms for consultations. Communication could likewise be through devices that permit you to forward images and get a conclusion.
Teleophthalmology: Telemedicine platforms permit ophthalmologists to examine a patient’s eyes and treat diseases remotely.
Telepathology: Pathologists get images and videos for diagnosis, research, and patient treatment, subsequently eliminating the requirement for physical interaction.
Teleobstetrics: Obstetricians can give pre-birth care without the requirement for physical contact by exchanging data for accurate diagnosis.
What services can be provided by Telemedicine Services
Telemedicine in healthcare can be utilized for a wide variety of health services. Here is a compiled list of common conditions that require an essential consideration from a doctor to get treated by Telemedicine.
- Allergies
- Joint Pain
- Asthma
- Bronchitis
- Colds and Flu
- Diarrhea
- Infections
- Insect Bites
- Pharyngitis
- Conjunctivitis
- Rashes
- Respiratory Infections
- Sinusitis
- Skin Inflammations
- Cellulitis
- Sore Throats
- Sprains & StrainsBladder Infections
- UTIs
- Sports Injuries
- Vomiting
Telemedicine services can range widely by specialty. A specialist could utilize the Telemedicine platform to do post-operation check-ins with patients to ensure their injury isn’t infected. A gynecologist could utilize a live telemedicine solution for giving birth control counseling. An endocrinologist might do live video chats with patients to examine recent lab results and answer questions.
Telemedicine Services Regulations
Telemedicine guidelines are constantly changing because clinical affiliations continuously develop new rules for telemedicine practices. For the most part, the state lays out these regulations, and they are as per the following:
Parity Laws
Just 29 states, including the District of Columbia, have passed parity laws into Telemedicine, and it guarantees private payers reimbursement for Telemedicine. Still, the specific limitations on this payment vary by state.
Patient-Informed Consent
Patient-informed consent is obtained after the patient finds out about telemedicine services, and only a few states require it.
Cross-state licensing
Cross-state licensing permits doctors to take care of patients not situated in the state where they got their license. A few states are attempting to layout measures that will put this into impact.
Pre-Exiting Physician-Patient Relationship
A few states make it mandatory for any patient utilizing Telemedicine to have previously paid a physical visit to the healthcare institution.
Online Prescribing
States have guidelines limiting which prescriptions doctors can recommend online.
Barriers to Telemedicine Services
- It tends to be a tedious cycle to change laws in states where parity laws don’t exist.
- Staff training and gear costs for Telemedicine may not be in the institution’s budget and may strain their funds.
- State-licensing necessities won’t permit doctors to treat patients across the boundaries of their state, subsequently restricting Telemedicine’s abilities.
- Repayment Policy for Telemedicine isn’t as clearly-defined as face-to-face visits and is in a consistent state of flux.
HIPAA and Telemedicine Services
All telemedicine solutions must be HIPAA compliant and give a high-security medium to their patient’s information. Not every video consultation software is appropriate for discussions. The picked software should be safe and secure.
Telemedicine Services Terms
Broadband: Broadband is a communication framework that can send various frequencies, typically microwave, broadcast, or satellite TV.
Encryption: Encoding information so just those with authorization can gain access.
Clinical Information System: This is hospital portal development-based data that has to do with patient care and not regulatory information.
Video conferencing: This is the transmission of video pictures and audio over significant distances.
Electronic health record: A collection of delicate data about a patient’s health sent to other healthcare facilities for telemedical purposes.
Step-by-step process of telemedicine app development
Once you’re aware of what is telemedicine, here’s the step-by-step process to follow:
1. Define project requirements
To comprehend the needs of your project, the telemedicine solutions that are currently available, and the regulatory requirements, conduct market research. Establish the goals of your telemedicine app, such as keeping track of medical information and enabling video consultations.
2. Design user interface
To check the application’s usability and design, create mockups and wireframes. Build an easily understandable and highly intuitive interface that works efficiently. Additionally, pay attention to accessibility so that it can be accessed by older adults or people with impairments.
3. Develop backend infrastructure
Establish a secure backend architecture to manage processing and data storage. Use a cloud platform or server hosting solution for optimal data protection and scalability. To secure data, robust security mechanisms, including access control, authentication, and encryption, should be put in place.
4. Integrate telemedicine app features
In the next step, develop a feature-rich application with secure messaging and video conferencing features. You may also integrate third-party APIs for excellent functionalities like payment processing and EHR integration.
5. Test and launch the app!
Test the program thoroughly to find and address any underlying issues so that the user experience is improved. Make sure the healthcare regulatory bodies grant you the required approvals. It’s time to release the software on app stores when it has fixed all bugs. You can promote it on different social media networks for maximum attention!
Get Your White Label Telemedicine Software Solution
The Future of Telehealth
Telehealth has a great future for both healthcare organizations and patients. Once we address legal and reimbursement issues, telemedicine can thrive across the country.
What’s Ahead for Telehealth?
- More People Using Telemedicine: Millions of Americans already use telemedicine, and this number is growing. With more patients and doctors embracing it, telemedicine is bound to expand.
- 24/7 Online Medical Centers: Picture a platform where patients, doctors, and staff can connect anytime. Remote doctors could treat patients from different locations using video calls and digital monitoring devices.
- International Collaboration: Telemedicine could break down international barriers, allowing doctors from different countries to share medical advancements.
- Increased Acceptance: As patients enjoy shorter wait times and easier access to care, they’ll become more comfortable with telemedicine. Doctors will see better patient outcomes and increased revenue without more work. Insurers like Medicaid, Medicare, and private payers will adapt to the demand.
- Better Health System Collaboration: Currently, sharing medical records between different systems is challenging. In the future, telehealth will improve this, making patient care smoother and billing more automated.
- Augmented Reality Mirrors: These mirrors, using advanced imaging, could help doctors diagnose eye, skin, and breast conditions more accurately.
Understanding Telemedicine Terms
- Telemedicine: Using technology to provide clinical services.
- Telehealth: Similar to telemedicine but includes all health services, like nurse education through video calls.
- Digital Medical Devices: Devices like blood pressure cuffs and glucometers that can send data electronically.
- Distant Site: Where the doctor is located during the telemedicine service. Important for understanding reimbursement.
- Electronic Medical Record (EMR): Digital storage of patient records within one healthcare organization.
- Electronic Health Record (EHR): A digital record of patient information shared across different healthcare settings.
- Encryption: A method to protect electronic data so only authorized people can access it.
- HIPAA: Laws that protect patient information.
- Originating Site: Where the patient is during a telemedicine service, relevant for Medicaid reimbursement.
- Remote Monitoring: Using digital devices to send patient data to doctors in real-time.
- Video Conferencing: Real-time video communication between multiple locations.
Conclusion
Telemedicine software are designed to tackle different challenges experienced by healthcare providers and patients. With the sudden outbreak of COVID, the need for telemedicine software increased as travel was restricted. In the coming years, telemedicine software is expected to become the future of the healthcare industry. If you want to bring your healthcare services online, get in touch with experts at VCDoctor! It is a famous telemedicine platform building feature-rich and robust platforms. To know more, connect with experts now! We hope this article helped you understand what is telemedicine!
FAQs
1. List some common challenges experienced while developing a telemedicine app
Some commonly experienced challenges when developing a telemedicine application are finding the best team to build an application, the application’s UX and UI designs, and application safety and security.
2. What is telemedicine app development cost?
Generally, the telemedicine app development cost is different based on features. If you choose advanced features, the cost increases.
3. What significant factors should be considered when choosing a telemedicine app development team?
When choosing the best telemedicine app development team, some major factors to consider are:
- The team’s experience and expertise
- Technical understanding and proficiency
- Data security and compliance
- Application customization
4. List popular features of a telemedicine application
When building a telemedicine app, some must-have features are:
- Telemedicine appointment scheduling
- Video conferencing
- Electronic health records
- Prescription management.
5. Is telemedicine different from telehealth software?
Yes, telemedicine includes offering remote clinical services. In telehealth, different services, including clinical and nonclinical, such as educational, administrative meetings, and more, are included.
4. List popular features of a telemedicine application
When building a telemedicine app, some must-have features are:
- Telemedicine appointment scheduling
- Video conferencing
- Electronic health records
- Prescription management.
5. Is telemedicine different from telehealth software?
Yes, telemedicine includes offering remote clinical services. In telehealth, different services, including clinical and nonclinical, such as educational, administrative meetings, and more, are included.
For any query or discussion, feel free to connect with our healthcare experts, as they are always there for your help.




